[Electronics] Bachelor Thesis: Wireless Power Transfer
This article describe my Bachelor Thesis made back in 2017 at Zheijang University in China.
Objectives
The context of this project is the use rectenna in a wireless power transfer to convert microwave energy into DC power. The main goal is to reach the best conversion efficiency possible. To this end a constant tuning the load is made.
Methods | Experiences | Results
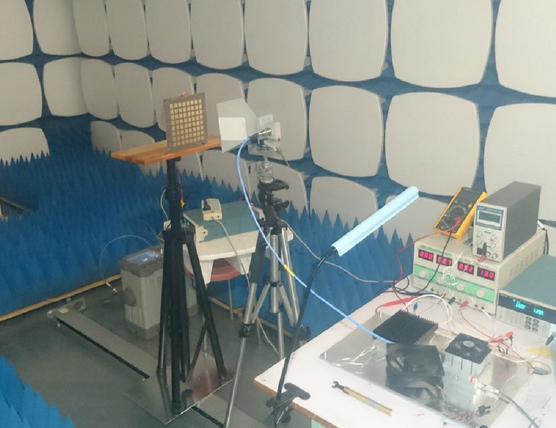
An array of 64 rectennas is used to receive RF power. This rectenna is subdivided into 16 sub-circuits of 4 rectennas in parallel connected to the same load. These loads are made with digital potentiometers, driven by SPI with a microcontroller. With a measure of each output voltage, the microcontroller can compute the DC power and find the optimum power point with an algorithm similar to MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) used for solar panel.
All these data can be sent with the help of a Bluetooth module to a computer with a supervision software. When the Bluetooth module is not enabled, the whole circuit is in low power mode and will consume less than 1% of the rectennas received power.
The system was tested with a horn antenna as transmitter and different input
power density. Even if the load range wasn’t tuned perfectly to track the maximum
efficiency point, a gain in power up to 10.43% has been measured with a
corresponding improvement of the RF to DC conversion efficiency of 4.65% with
low input power (-3.4 to 3.9 dBm for one rectenna unit).